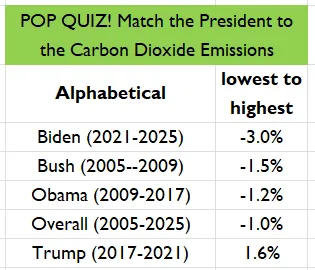
If green activists truly worried about atmospheric greenhouse gases (GHG) such as carbon dioxide, they would bring back plastic shopping bags tomorrow. But they wouldn’t – the whipped up plastic scare has been too useful a tool to batter people into accepting the relentless drive to embrace inferior products and technologies. The acceptance of reduced lifestyle choices, and the unlimited chance for middle class activists to virtue signal, is part of the all-important collectivisation under the planned Net Zero project. But now a recent science paper has revealed that in 15 out of 16 applications of plastic covering 90% of global volume, the alternatives actually produced more greenhouse gases.
And not just more, but significantly more. Over their lifetime cycle, paper bag substitutes produce at least four times more GHG emissions than their plastic counterparts. Paper bags are noted to weigh significantly more than plastic carriers leading to higher GHG emissions for production and transportation.
Talk about an inconvenient conclusion. The scientists found that in the 15 applications covering the five key sectors of packaging, building and construction, automobiles, textiles and consumer durable, plastic products released 10% to 90% fewer emissions across the product life cycle. “Furthermore,” the scientists observe, “in some applications, such as food packaging, no suitable alternatives to plastics exist.”
If carbon dioxide is your thing, and, of course, it is the crucial part of the reason for pursuing insane Net Zero policies, plastic needs to make a big comeback. But of course it will not. Despite revolutionising modern industrial life, it has the misfortune to be a hydrocarbon. Most plastics are a by-product from natural oil and gas production. Thus plastic bad, anything else good. The same blinkered thinking justifies the mass slaughter of any flying animal that is caught up in wind turbines, and the industrialisation of the seas at the expense of aquatic life such as whales and dolphins. In Germany, the hypocritical greens have even been in favour of tearing down parts of the forest setting for the mythical Brothers Grimm fairy tales. And we must not get started on road and bridge chomping EV cars. These are a true ecological disaster zone with a manufacturing requirement to turn over vast tracts of the Earth’s crust, and a small problem of insufficient children available to mine all the required cobalt in the Congo.
Of course, much play is made of the harmful disposal of plastic, but this is largely a waste management problem. There are plenty of ways to prudently recycle or dispose of plastic safely, but they come with some financial cost. If rich countries don’t want their plastic to end up in the oceans, they shouldn’t send it to poor countries who, out of sight, dump it in local rivers on their behalf. The scientists note that better disposal of plastics is an urgent challenge given the “threats to biodiversity and ecosystem health worldwide”.
The key table in the paper is reproduced below. It shows that the GHG emission impact in switching from plastic shopping bags to paper, the next best alternative, is 80% higher. The other 15 switches are also detailed with a note of the mostly much higher GHG impacts. The detailed methods used to calculate the plastic versus non-plastic alternatives are laid out in the paper, which is written by three scientists with expertise in sustainability and chemical and biological engineering from Sheffield and Cambridge Universities.
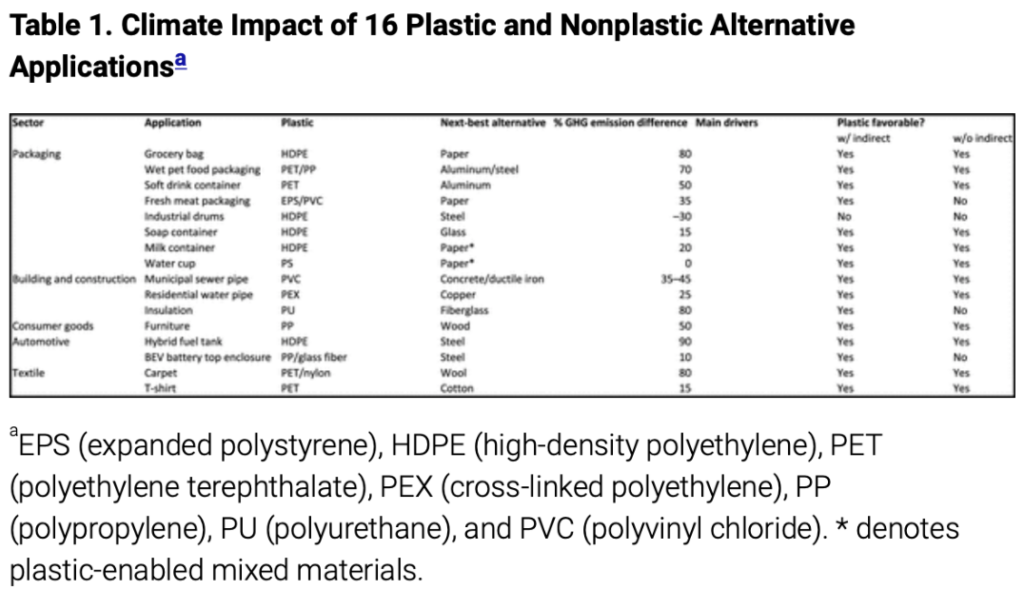
In arriving at their results, the authors considered many indirect impacts such as fuel saving in lighter cars, lower energy consumption in houses insulated with polyurethane and reduced food spoilage when using plastic packaging instead of butcher paper. Many advantages for the use of plastics were identified. Insulating with polyurethane is better than the alternatives and therefore reduces heating fuel consumption, while plastic tanks cut vehicle weight and thus are more fuel efficient. Meanwhile it is said that there are few alternatives to plastics in food production due to high levels of spoilage when using the alternatives. It might be noted that milkshakes and paper straws give an obvious illustration of the problems in using inferior substitutes.
It is reasonable to ask where all the virtuous green solutions to a politically-claimed ‘climate emergency’ will take us. Almost everything that is being forced through, whether it be demonising plastic to blanketing the land and seas with giant wind turbines, makes little sense. They often cause more ecological harm than good, while the fudged finances backing many of the projects might shame Charles Ponzi. It is becoming obvious that modern industrial society will collapse if the Net Zero tyranny is ever enforced.
Extremist greens from George Monbiot to Sir David Attenborough seem only too aware of the many inconsistencies in making changes to any human activity that has an ‘impact’ on the planet. Best, it seems, to have no impact at all, perhaps not be on the planet in the first place. At the moment their views seem to be shared by many influential elites pressing ahead with any number of decadent plans to drive those less well-off than themselves into abject poverty and depravation.
In 1999, Monbiot said flying across the Atlantic, “is now as unacceptable as child abuse”. The rhetoric has hardly diminished over 25 years with Monbiot recently ramping up his doomsday prose to call for an end to animal farming. Eating meat, eggs and milk is an “indulgence” the planet cannot afford, he claimed. How this Guardianista weirdo expects humans to survive on what is often a hostile planet is anyone’s guess.
Perhaps there ought to be fewer people on the planet for a start. This seems to be the opinion of the supreme middle class embodiment of green virtue, Sir David Attenborough. Supporting the neo-Malthusian Optimum Population Trust, he said in 2009 that he hadn’t seen a problem that “wouldn’t be easier to solve with fewer people”. In 2013, he was reported to have observed that sending food to famine-ridden countries is “barmy”. Using the example of Ethiopia, he said the famine there was caused by “too many people for too little piece of land”.
Chris Morrison is the Daily Sceptic’s Environment Editor.