It’s an emergency! Green plants spreading at alarming rate in Antarctica
By Jo Nova
Lesson #457 in how to lie with science
File this lesson away in the Decline and Fall of Enlightenment Science. Nature, formerly known as the esteemed science journal, is now achieving everything a captured tabloid industry sales mag could hope for. They’ve squeezed a disaster out of a tiny change in a short record, and from a good news story. Let’s not forget, for the last 100,000 years most humans would have been happy that a bit of Antarctica was greening.
“Lush”? The only people who call this lush are penguins:
To appreciate the Black Belt level of naked exaggeration going on here, consider the opening hyperbole:
A fast-warming region of Antarctica is getting greener with shocking speed. Satellite imagery of the region reveals that the area covered by plants increased by almost 14 times over 35 years — a trend that will spur rapid change of Antarctic ecosystems.
“It’s the beginning of dramatic transformation,” says Olly Bartlett, a remote-sensing specialist at the University of Hertfordshire in Hatfield, UK, and an author of the study1, published today in Nature Geoscience, that reports these results.
All this shock and drama arise from an area of “less than a square kilometer” expanding all the way up to “nearly 12 square kilometers”. These numbers “shocked us” say the PR team, I mean, the scientists, who continue on in their best Agony-Aunt impression: “It’s simply that rate of change in an extremely isolated, extremely vulnerable area that causes the alarm.” Sob sob, and Boo hoo too. It’s a lonely peninsula. Can we find it a friend?
Everything about this shows the pathetic decay of Western Science. We’re talking about 12 square kilometers of more habitable land on a continent with 14 million square kilometers of ice. The horrible affliction of unexpected tundra now covers 0.00009% of Antarctica.
It could get worse, the mosses might make … soil:
The research is “really important”, says Jasmine Lee, a conservation scientist at the British Antarctic Survey in Cambridge, UK. Other studies2,3 have found evidence that vegetation on the peninsula is changing in response to climate change, “but this is the first study that’s taken a huge-scale approach to look at the entire region”, she says.
Previous visits to the peninsula led the authors to think that most of the vegetation is moss. As mosses spread to previously ice-covered landscapes, they will build up a layer of soil, offering a habitat for other plant life, Roland says. “There’s a huge potential here to see a further increase in the amount of non-native, potentially invasive species,” he says.
It is, of course, due to climate change:
The researchers point to climate change as the driver of the landscape’s shift from white to green. Temperatures on the peninsula have risen by almost 3 °C since 1950, which is a much bigger increase than observed across most parts of the planet.
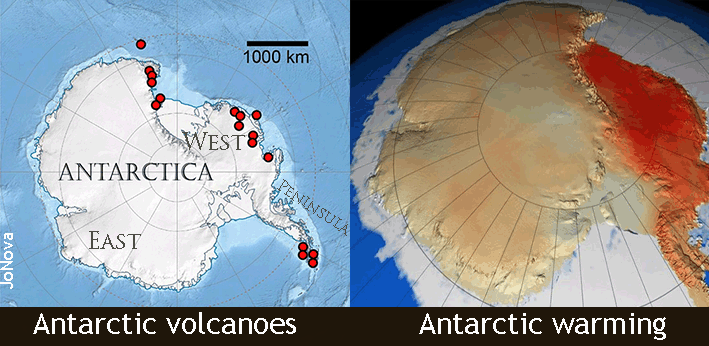
Nobody mention the 91 volcanoes they discovered there seven years ago which line up with the warmest parts of Antarctica. We sit on a ball of lava, and there is an edge of crustal plate under there. But really, it’s more likely the warming is caused by your Ford fiesta and those beef kebabs…
Quick, someone build a wind farm to kill off this feral moss!